| vlsitechnology.org /IR drop /example 1 /check |
Check |
IR Drop
We can check the result by using the strap widths and other chip specs to calculate the power that can be delivered. We use the procedure shown previously.
Step 1: Estimate Vcore using Ipad=50mA:
| Vcore = |
|
||||||
| = | 1.17×(1−2×0.050×(0.022+0.02+0.04)⁄1.2 | ||||||
| = | 1.162V |
Step 2: Calculate the reference power supply conductance G:
| G = |
|
|||
| = | 7 ⁄ (4 × 0.06) = | 29.17 mhos |
Step 3 is to set out the values of kan, kwn, kcn and mn for each metal layer, and use these to calculate the value of L.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ¹75%=.06/.08; ²300%=.06/.02 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
From which
| L = | kw1kc1(1-ps)(1-m1(1-ka2p)(1-ka3p))+ |
| kw2kc2(1-m2(1-ka2p)(1-ka3p))+ | |
| kw3kc3(1-m3(1-ka2p)(1-ka3p))+ | |
| kw4kc4(1-m4(1-ka2p)(1-ka3p))+ | |
| kw5kc5(1-m5(1-ka2p)(1-ka3p))+ | |
| kw6kc6(1-m6(1-ka2p)(1-ka3p)) | |
| = | ( 0.20 + 0.44 + 0.50 + 0.44 + 0.72 + 4.05 ) |
| = | 6.35 |
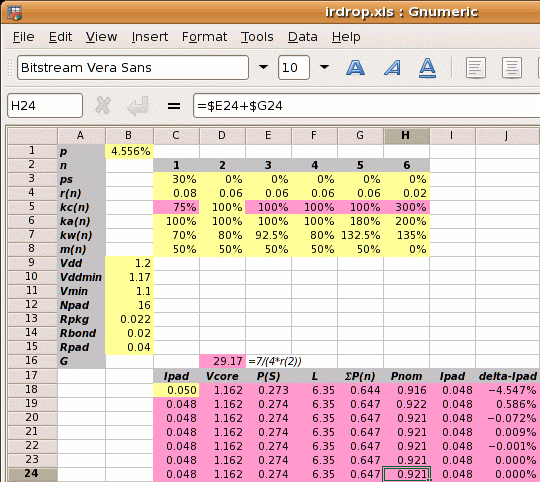
Step 4: Calculate Pnom. Pnom depends on the value of Ipad which we don't know, so we start with Ipad=50mA which gives us Vcore, then Pnom and a new value of Ipad. We use a spreadsheet to iterate to the solution. The yellow squares mark user input and the pink squares are calculated values. The first estimate for Pnom is shown below.
| m1′ = | m1×(1-ka2p)(1-ka3p) |
| Pnom= |
|
|||||
| = |
|
|||||
| = | 2.226×(0.123+0.289) = 0.916W |
The iteration leads to the solution of Pnom=0.921W. This is slightly higher than the 0.9W of the example, which we expect because the power strap allocation percentage has been made slightly higher by the rounding up process.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ¹ p = 1−3.502/3.670 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||